|
| 發表者 |
討論內容 |
冷日
(冷日) |
發表時間:2019/7/11 16:34 |
- Webmaster


- 註冊日: 2008/2/19
- 來自:
- 發表數: 15773
|
- [轉貼]JAVA 使用 easyexcel 操作 Excel
JAVA使用easyexcel操作Excel之前寫過一篇《 JAVA操作Excel》,介紹了 jxl和 poi讀寫Excel的實現,今天為大家介紹一下使用 easyexcel對Excel進行讀寫,項目主頁地址: https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel 作者對easyexcel的介紹是: Java解析、生成Excel比較有名的框架有Apache poi、jxl。但他們都存在一個嚴重的問題就是非常的耗內存,poi有一套SAX模式的API可以一定程度的解決一些內存溢出的問題,但POI還是有一些缺陷,比如07版Excel解壓縮以及解壓後存儲都是在內存中完成的,內存消耗依然很大。easyexcel重寫了poi對07版Excel的解析,能夠原本一個3M的excel用POI sax依然需要100M左右內存降低到KB級別,並且再大的excel不會出現內存溢出,03版依賴POI的sax模式。在上層做了模型轉換的封裝,讓使用者更加簡單方便
使用easyexcel,首先我們需要添加maven依賴: dependency>
groupId>
artifactId>
version>
dependency> 首先,我們先來看看如何寫Excel,寫入Excel,我們可以通過 com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter類實現,下面我們來看一下最簡單的無表頭的實現 package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
ExcelWriteTest {
/**
* 每行數據是List<String>無表頭
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
throws IOException {
);) {
ExcelWriter writer = false);
Sheet sheet1 = 0);
sheet1.setSheetName();
List<List<String>> data = new ArrayList<>();
100; i++) {
List<String> item = new ArrayList<>();
item.add( + i);
item.add( + i);
item.add( + i);
data.add(item);
}
writer.write0(data, sheet1);
writer.finish();
}
}
} 生成的Excel樣式如下:
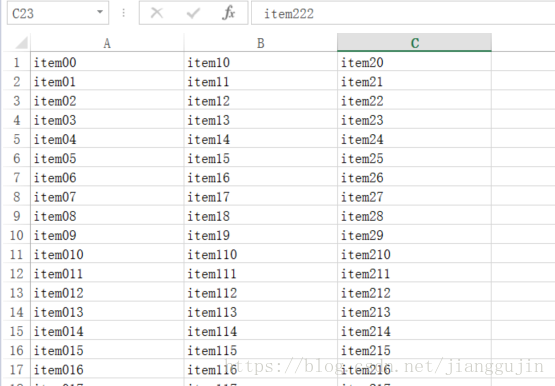 很多時候,我們在生成Excel的時候都是需要添加表頭的,使用easyexcel可以很容易的實現,我們可以對上面的例子進行簡單的改造,為其添加表頭 package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
throws IOException {
);) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = 0);
sheet1.setSheetName();
List<List<String>> data = new ArrayList<>();
100; i++) {
List<String> item = new ArrayList<>();
item.add( + i);
item.add( + i);
item.add( + i);
data.add(item);
}
List<List<String>> head = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> headCoulumn1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn2 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn3 = new ArrayList<String>();
headCoulumn1.add();
headCoulumn2.add();
headCoulumn3.add();
head.add(headCoulumn1);
head.add(headCoulumn2);
head.add(headCoulumn3);
Table table = 1);
table.setHead(head);
writer.write0(data, sheet1, table);
writer.finish();
}
}
} 效果如下: 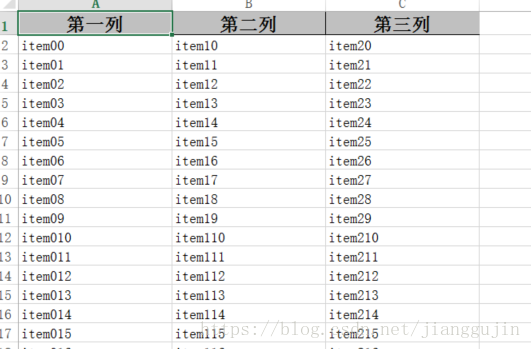 除了上面添加表頭的方式,我們還可以使用實體類,為其添加 com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty註解來生成表頭,實體類數據作為Excel數據 package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
throws IOException {
);) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = 0, ExcelPropertyIndexModel.class);
sheet1.setSheetName();
List<ExcelPropertyIndexModel> data = new ArrayList<>();
100; i++) {
ExcelPropertyIndexModel item = new ExcelPropertyIndexModel();
item.name = + i;
item.age = + i;
item.email = + i;
item.address = + i;
item.sax = + i;
item.heigh = + i;
item.last = + i;
data.add(item);
}
writer.write(data, sheet1);
writer.finish();
}
}
BaseRowModel {
0)
private String name;
1)
private String age;
2)
private String email;
3)
private String address;
4)
private String sax;
5)
private String heigh;
6)
private String last;
getName() {
return name;
}
setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
getAge() {
return age;
}
setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
getEmail() {
return email;
}
setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
getAddress() {
return address;
}
setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
getSax() {
return sax;
}
setSax(String sax) {
this.sax = sax;
}
getHeigh() {
return heigh;
}
setHeigh(String heigh) {
this.heigh = heigh;
}
getLast() {
return last;
}
setLast(String last) {
this.last = last;
}
}
} 效果如下:
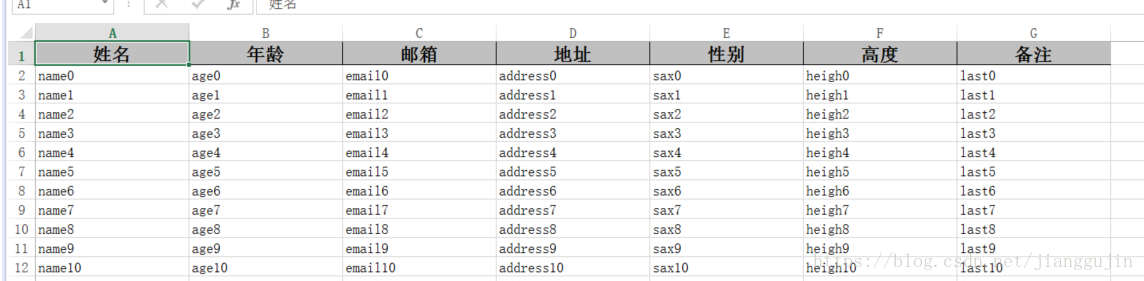 如果單行表頭表頭還不滿足需求,沒關係,還可以使用多行複雜的表頭 package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
throws IOException {
);) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = 0, MultiLineHeadExcelModel.class);
sheet1.setSheetName();
List<MultiLineHeadExcelModel> data = new ArrayList<>();
100; i++) {
MultiLineHeadExcelModel item = new MultiLineHeadExcelModel();
item.p1 = + i;
item.p2 = + i;
item.p3 = + i;
item.p4 = + i;
item.p5 = + i;
item.p6 = + i;
item.p7 = + i;
item.p8 = + i;
item.p9 = + i;
data.add(item);
}
writer.write(data, sheet1);
writer.finish();
}
}
BaseRowModel {
0)
private String p1;
1)
private String p2;
2)
private String p3;
3)
private String p4;
4)
private String p5;
5)
private String p6;
6)
private String p7;
7)
private String p8;
8)
private String p9;
getP1() {
return p1;
}
setP1(String p1) {
this.p1 = p1;
}
getP2() {
return p2;
}
setP2(String p2) {
this.p2 = p2;
}
getP3() {
return p3;
}
setP3(String p3) {
this.p3 = p3;
}
getP4() {
return p4;
}
setP4(String p4) {
this.p4 = p4;
}
getP5() {
return p5;
}
setP5(String p5) {
this.p5 = p5;
}
getP6() {
return p6;
}
setP6(String p6) {
this.p6 = p6;
}
getP7() {
return p7;
}
setP7(String p7) {
this.p7 = p7;
}
getP8() {
return p8;
}
setP8(String p8) {
this.p8 = p8;
}
getP9() {
return p9;
}
setP9(String p9) {
this.p9 = p9;
}
}
} 效果如下:
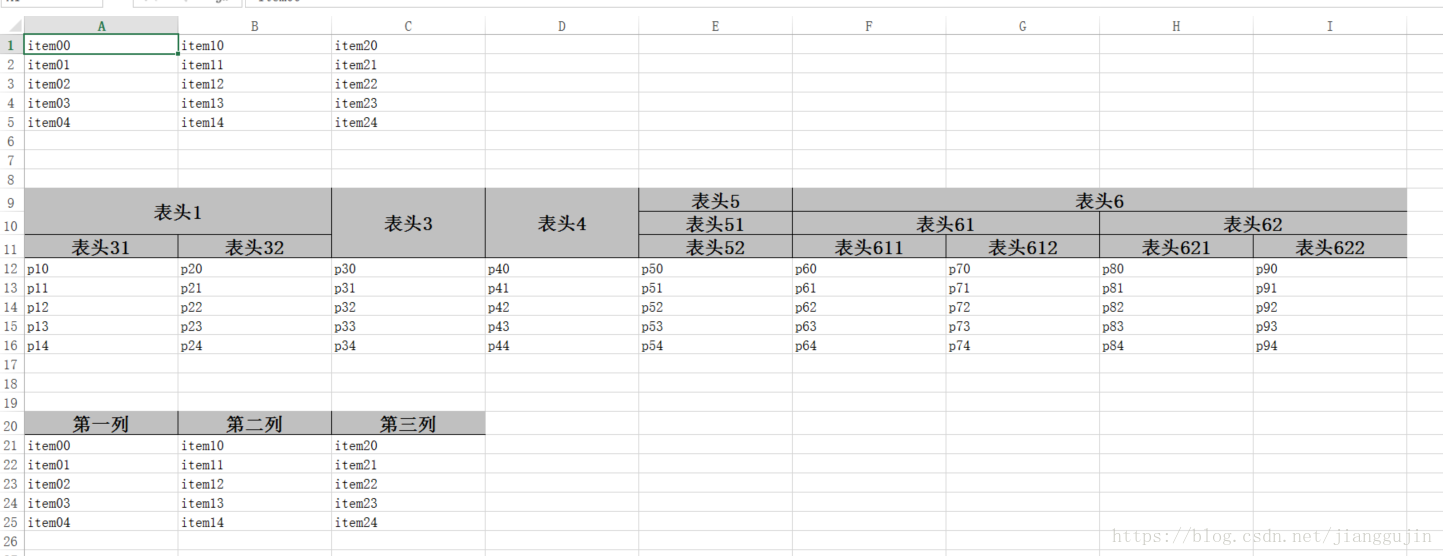
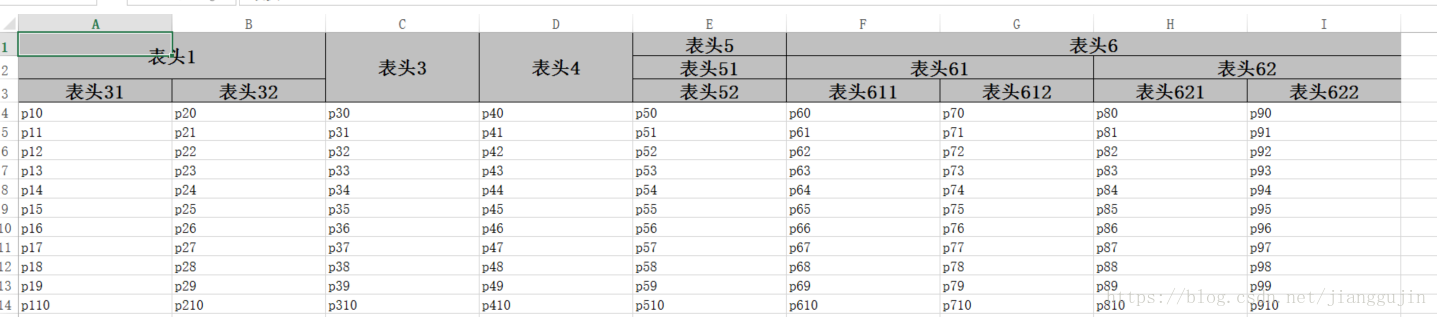 怎麼樣,這些已經基本滿足我們的日常需求了,easyexcel不僅支持上述幾種形式,還支持在一個sheet中添加多個表 package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
throws IOException {
);) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = 0);
sheet1.setSheetName();
// 數據全是List<String> 無模型映射關係
Table table1 = 1);
List<List<String>> data1 = new ArrayList<>();
5; i++) {
List<String> item = new ArrayList<>();
item.add( + i);
item.add( + i);
item.add( + i);
data1.add(item);
}
writer.write0(data1, sheet1, table1);
// 模型上有表頭的註解
Table table2 = 2);
table2.setClazz(MultiLineHeadExcelModel.class);
List<MultiLineHeadExcelModel> data2 = new ArrayList<>();
5; i++) {
MultiLineHeadExcelModel item = new MultiLineHeadExcelModel();
item.p1 = + i;
item.p2 = + i;
item.p3 = + i;
item.p4 = + i;
item.p5 = + i;
item.p6 = + i;
item.p7 = + i;
item.p8 = + i;
item.p9 = + i;
data2.add(item);
}
writer.write(data2, sheet1, table2);
// 模型上沒有註解,表頭數據動態傳入,此情況下模型field順序與excel現實順序一致
List<List<String>> head = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> headCoulumn1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn2 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn3 = new ArrayList<String>();
headCoulumn1.add();
headCoulumn2.add();
headCoulumn3.add();
head.add(headCoulumn1);
head.add(headCoulumn2);
head.add(headCoulumn3);
Table table3 = 3);
table3.setHead(head);
writer.write0(data1, sheet1, table3);
writer.finish();
}
}
BaseRowModel {
0)
private String p1;
1)
private String p2;
2)
private String p3;
3)
private String p4;
4)
private String p5;
5)
private String p6;
6)
private String p7;
7)
private String p8;
8)
private String p9;
getP1() {
return p1;
}
setP1(String p1) {
this.p1 = p1;
}
getP2() {
return p2;
}
setP2(String p2) {
this.p2 = p2;
}
getP3() {
return p3;
}
setP3(String p3) {
this.p3 = p3;
}
getP4() {
return p4;
}
setP4(String p4) {
this.p4 = p4;
}
getP5() {
return p5;
}
setP5(String p5) {
this.p5 = p5;
}
getP6() {
return p6;
}
setP6(String p6) {
this.p6 = p6;
}
getP7() {
return p7;
}
setP7(String p7) {
this.p7 = p7;
}
getP8() {
return p8;
}
setP8(String p8) {
this.p8 = p8;
}
getP9() {
return p9;
}
setP9(String p9) {
this.p9 = p9;
}
}
} 效果如下:
 如果表頭的樣式不滿足我們的需求,需要調整,我們可以使用 com.alibaba.excel.metadata.TableStyle定義我們需要的樣式,然後調用table對象的 setTableStyle方法進行設置。 好了,到這裡寫入excel就基本介紹完了,下面我們就來看看如何讀取excel,實際上現在的這個版本( 1.0.1)在讀取的時候是有BUG的,讀取03版的 .xls格式的excel正常,但是讀取07版的 .xlsx版的excel就會出異常,原因是在解析的時候sheet臨時文件路徑拼裝有誤,下面是我針對這個版本修復後的實現,大家可以替換掉原包中的實現 package com.alibaba.excel.read;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.v07.RowHandler;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.v07.XmlParserFactory;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.v07.XMLTempFile;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.exception.ExcelAnalysisException;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.util.FileUtil;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.model.SharedStringsTable;
import org.apache.xmlbeans.XmlException;
import org.openxmlformats.schemas.spreadsheetml.x2006.main.CTWorkbook;
import org.openxmlformats.schemas.spreadsheetml.x2006.main.CTWorkbookPr;
import org.openxmlformats.schemas.spreadsheetml.x2006.main.WorkbookDocument;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.ContentHandler;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
BaseSaxAnalyser {
private SharedStringsTable sharedStringsTable;
new LinkedList<String>();
new ArrayList<SheetSource>();
false;
final String path;
private File tmpFile;
private String workBookXMLFilePath;
private String sharedStringXMLFilePath;
throws Exception {
this.analysisContext = analysisContext;
this.path = XMLTempFile.createPath();
new File(XMLTempFile.getTmpFilePath(path));
this.workBookXMLFilePath = XMLTempFile.getWorkBookFilePath(path);
this.sharedStringXMLFilePath = XMLTempFile.getSharedStringFilePath(path);
start();
}
@Override
execute() {
try {
Sheet sheet = analysisContext.getCurrentSheet();
if (!isAnalysisAllSheets(sheet)) {
0) {
return;
}
InputStream sheetInputStream = 1).getInputStream();
parseXmlSource(sheetInputStream);
return;
}
0;
this.sheetSourceList) {
i++;
new Sheet(i));
parseXmlSource(sheetSource.getInputStream());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
stop();
new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
} finally {
}
}
isAnalysisAllSheets(Sheet sheet) {
null) {
true;
}
0) {
true;
}
false;
}
stop() {
FileUtil.deletefile(path);
}
parseXmlSource(InputStream inputStream) {
try {
ContentHandler handler = this.analysisContext,
sharedStringList);
XmlParserFactory.parse(inputStream, handler);
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
}
}
getSheets() {
List<Sheet> sheets = new ArrayList<Sheet>();
try {
1;
this.sheetSourceList) {
Sheet sheet = 0);
sheet.setSheetName(sheetSource.getSheetName());
i++;
sheets.add(sheet);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
stop();
new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
} finally {
}
return sheets;
}
throws IOException, XmlException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException {
createTmpFile();
unZipTempFile();
initSharedStringsTable();
initUse1904WindowDate();
initSheetSourceList();
}
throws FileNotFoundException {
FileUtil.writeFile(tmpFile, analysisContext.getInputStream());
}
throws IOException {
FileUtil.doUnZip(path, tmpFile);
}
throws IOException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException {
new ArrayList<SheetSource>();
InputStream workbookXml = this.workBookXMLFilePath);
XmlParserFactory.parse(workbookXml, new DefaultHandler() {
@Override
throws SAXException {
)) {
String name = null;
0;
0; i < attrs.getLength(); i++) {
)) {
name = attrs.getValue(i);
} id = Integer.parseInt(attrs.getValue(i).replaceAll("rId", ""));
try {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(XMLTempFile.getSheetFilePath(path, id));
sheetSourceList.add(new SheetSource(id, name, inputStream));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} **/
//應該使用sheetId屬性
)) {
id = Integer.parseInt(attrs.getValue(i));
try {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(XMLTempFile.getSheetFilePath(path, id));
sheetSourceList.add(new SheetSource(id, name, inputStream));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
});
workbookXml.close();
// 排序後是倒序,不符合實際要求
// Collections.sort(sheetSourceList);
Collections.sort(sheetSourceList, new Comparator<SheetSource>() {
@Override
compare(SheetSource o1, SheetSource o2) {
return o1.id - o2.id;
}
});
}
throws IOException, XmlException {
InputStream workbookXml = new FileInputStream(workBookXMLFilePath);
WorkbookDocument ctWorkbook = WorkbookDocument.Factory.parse(workbookXml);
CTWorkbook wb = ctWorkbook.getWorkbook();
CTWorkbookPr prefix = wb.getWorkbookPr();
null) {
this.use1904WindowDate = prefix.getDate1904();
}
this.analysisContext.setUse1904WindowDate(use1904WindowDate);
workbookXml.close();
}
throws IOException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException {
//因為sharedStrings.xml文件不一定存在,所以在處理之前增加判斷
File sharedStringXMLFile = this.sharedStringXMLFilePath);
if (!sharedStringXMLFile.exists()) {
return;
}
InputStream inputStream = this.sharedStringXMLFilePath);
//this.sharedStringsTable = new SharedStringsTable();
//this.sharedStringsTable.readFrom(inputStream);
XmlParserFactory.parse(inputStream, new DefaultHandler() {
@Override
int length) {
sharedStringList.add(new String(ch, start, length));
}
});
inputStream.close();
}
SheetSource> {
int id;
private String sheetName;
private InputStream inputStream;
int id, String sheetName, InputStream inputStream) {
this.id = id;
this.sheetName = sheetName;
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
getSheetName() {
return sheetName;
}
setSheetName(String sheetName) {
this.sheetName = sheetName;
}
getInputStream() {
return inputStream;
}
setInputStream(InputStream inputStream) {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
getId() {
return id;
}
int id) {
this.id = id;
}
compareTo(SheetSource o) {
this.id) {
0;
} this.id) {
1;
} else {
1;
}
}
}
} 另外,使用easyexcel讀取excel的時候需要設置excel的版本,但是有些時候我們無法預知excel的版本,所以個人感覺這樣不是太好,所以模仿 poi寫了一個用於獲取 com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader對象的工具類 package com.alibaba.excel.read;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PushbackInputStream;
import org.apache.poi.EmptyFileException;
import org.apache.poi.openxml4j.exceptions.InvalidFormatException;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.DocumentFactoryHelper;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.NPOIFSFileSystem;
import org.apache.poi.util.IOUtils;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
ExcelReaderFactory {
/**
* @param in
* 文件輸入流
* @param customContent
* 自定義模型可以在
* {@link AnalysisEventListener#invoke(Object, AnalysisContext) }
* AnalysisContext中獲取用於監聽者回調使用
* @param eventListener
* 用戶監聽
* @throws IOException
* @throws EmptyFileException
* @throws InvalidFormatException
*/
getExcelReader(InputStream in, Object customContent,
AnalysisEventListener<?> eventListener) throws EmptyFileException, IOException, InvalidFormatException {
// 如果輸入流不支持mark/reset,需要對其進行包裹
if (!in.markSupported()) {
in = 8);
}
// 確保至少有一些數據
byte[] header8 = IOUtils.peekFirst8Bytes(in);
ExcelTypeEnum excelTypeEnum = null;
if (NPOIFSFileSystem.hasPOIFSHeader(header8)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLS;
}
if (DocumentFactoryHelper.hasOOXMLHeader(in)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX;
}
null) {
new ExcelReader(in, excelTypeEnum, customContent, eventListener);
}
);
}
/**
* @param in
* 文件輸入流
* @param customContent
* 自定義模型可以在
* {@link AnalysisEventListener#invoke(Object, AnalysisContext) }
* AnalysisContext中獲取用於監聽者回調使用
* @param eventListener
* 用戶監聽
* @param trim
* 是否對解析的String做trim()默認true,用於防止 excel中空格引起的裝換報錯。
* @throws IOException
* @throws EmptyFileException
* @throws InvalidFormatException
*/
getExcelReader(InputStream in, Object customContent,
AnalysisEventListener<?> eventListener, boolean trim)
throws EmptyFileException, IOException, InvalidFormatException {
// 如果輸入流不支持mark/reset,需要對其進行包裹
if (!in.markSupported()) {
in = 8);
}
// 確保至少有一些數據
byte[] header8 = IOUtils.peekFirst8Bytes(in);
ExcelTypeEnum excelTypeEnum = null;
if (NPOIFSFileSystem.hasPOIFSHeader(header8)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLS;
}
if (DocumentFactoryHelper.hasOOXMLHeader(in)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX;
}
null) {
new ExcelReader(in, excelTypeEnum, customContent, eventListener, trim);
}
);
}
} 下面我們就來寫一個簡單的讀取Excel的示例: package test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.ExcelReaderFactory;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.event.AnalysisEventListener;
ExcelReadTest {
@Test
throws Exception {
);) {
AnalysisEventListener<List<String>> listener = new AnalysisEventListener<List<String>>() {
@Override
invoke(List<String> object, AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println( + object);
}
@Override
doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println();
}
};
ExcelReader excelReader = ExcelReaderFactory.getExcelReader(in, null, listener);
excelReader.read();
}
}
} 正如寫入Excel的時候可以使用數據模型一樣,在讀取Excel的時候也可以直接將數據映射為模型對象,區別在於要使用 ExcelReader #read的重載方法。 package test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.ExcelReaderFactory;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.event.AnalysisEventListener;
ExcelReadTest {
@Test
throws Exception {
);) {
AnalysisEventListener<ExcelPropertyIndexModel> listener = new AnalysisEventListener<ExcelPropertyIndexModel>() {
@Override
invoke(ExcelPropertyIndexModel object, AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println( + object);
}
@Override
doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println();
}
};
ExcelReader excelReader = ExcelReaderFactory.getExcelReader(in, null, listener);
// 第二個參數為表頭行數,按照實際設置
excelReader.read(1, ExcelPropertyIndexModel.class));
}
}
BaseRowModel {
0)
private String name;
1)
private String age;
2)
private String email;
3)
private String address;
4)
private String sax;
5)
private String heigh;
6)
private String last;
getName() {
return name;
}
setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
getAge() {
return age;
}
setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
getEmail() {
return email;
}
setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
getAddress() {
return address;
}
setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
getSax() {
return sax;
}
setSax(String sax) {
this.sax = sax;
}
getHeigh() {
return heigh;
}
setHeigh(String heigh) {
this.heigh = heigh;
}
getLast() {
return last;
}
setLast(String last) {
this.last = last;
}
@Override
toString() {
+ address
+ ;
}
}
} 以上就是關於easyexcel的使用方法介紹,如有疑問,歡迎交流指正。
原文出處: JAVA使用easyexcel操作Excel - 蒋固金(jianggujin)的专栏 - CSDN博客
|
|
|
|
|
冷日
(冷日) |
發表時間:2019/7/11 16:37 |
- Webmaster


- 註冊日: 2008/2/19
- 來自:
- 發表數: 15773
|
- [轉貼]Java 使用 easyExcel 操作 Excel 案例
Java使用easyExcel操作Excel案例 這兩天一直在玩些小工具,今天整了下阿里巴巴的easyExcel,下面是案例:
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TestExcel {
@Test
public void testRead() throws FileNotFoundException {
InputStream inputStream =getInputStream("C:\\Users\\LiGe\\Desktop\\test.xls");
try {
ExcelReader reader = new ExcelReader(inputStream, ExcelTypeEnum.XLS, null, new AnalysisEventListener() {
@Override
public void invoke(Object o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("當前sheet"+analysisContext.getCurrentSheet().getSheetNo()+ " 當前行:" + analysisContext.getCurrentRowNum()
+ " data:" + o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
}
});
reader.read();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void testWriter() throws FileNotFoundException {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\LiGe\\Desktop\\test.xls");
try {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out,ExcelTypeEnum.XLS);
//寫第一個sheet
Sheet sheet = new Sheet(2,3,ImportInfo.class);
writer.write(getDate(),sheet);
for (ImportInfo in: getDate()
) {
System.out.println(in.getName());
}
writer.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public List<ImportInfo> getDate(){
List<ImportInfo> list = new ArrayList<ImportInfo>();
ImportInfo info = new ImportInfo();
info.setAge(12);
info.setName("zhangsan");
info.setEmail("11111@qq.com");
ImportInfo info1 = new ImportInfo();
info1.setAge(12);
info1.setName("zhangsan1");
info1.setEmail("11111@qq.com");
ImportInfo info2 = new ImportInfo();
info2.setAge(12);
info2.setName("zhangsan2");
info2.setEmail("11111@qq.com");
list.add(info);list.add(info1);list.add(info2);
return list;
}
private InputStream getInputStream(String fileName) {
try {
return new FileInputStream(new File(fileName));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
上面是測試類,這是實體類:
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
public class ImportInfo extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(index = 0)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(index = 1)
private Integer age;
@ExcelProperty(index = 2)
private String email;
/*
通過 @ExcelProperty 註解與 index 變量可以標注成員變量所映射的列
作為Excel的模型對像,需要setter方法
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
原文出處: Java使用easyExcel操作Excel案例 - IT人利哥的博客 - CSDN博客
|
|
|
冷日
(冷日) |
發表時間:2019/7/11 16:42 |
- Webmaster


- 註冊日: 2008/2/19
- 來自:
- 發表數: 15773
|
- [轉貼]史上最全的 Excel 導入導出之 easyexcel
史上最全的Excel導入導出之easyexcel喝水不忘挖井人,感謝阿里巴巴項目組提供了easyexcel工具類,github地址: https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel 環境搭建 - easyexcel 依賴(必須)
- springboot (不是必須)
- lombok (不是必須)
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
讀取excel文件
小於1000行數據 默認讀取讀取Sheet1的全部數據 ;
List;
指定讀取
下面是學生表.xlsx中Sheet1,Sheet2的數據
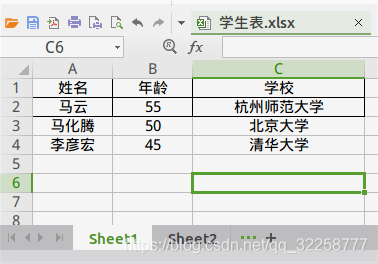
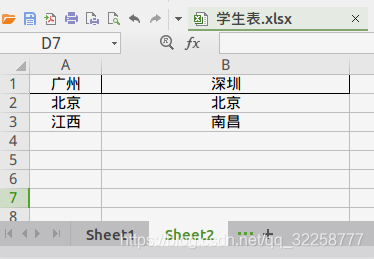
獲取Sheet1表頭以下的信息 ;
//第一個1代表sheet1, 第二個1代表從第幾行開始讀取數據,行號最小值為0
Sheet sheet ;
List;
獲取Sheet2的所有信息 ;
Sheet sheet ;
List;
大於1000行數據
默認讀取;
List;
指定讀取
;
Sheet sheet ;
List;
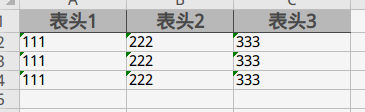
導出excle
單個Sheet導出 無模型映射導出;
List;
data;
data;
data;
List;
ExcelUtil;
結果
 模型映射導出1、定義好模型對像 ;
;
;
;
;
/**
* @description:
* @author: chenmingjian
* @date: 19-4-3 14:44
*/
)
@Data
{
/**
* value: 表頭名稱
* index: 列的號, 0表示第一列
*/
)
;
)
;
)
;
}
2、調用方法 ;
ArrayList;
{
TableHeaderExcelProperty tableHeaderExcelProperty ;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
data;
}
ExcelUtil;
多個Sheet導出
1、定義好模型對像 ;
;
;
;
;
/**
* @description:
* @author: chenmingjian
* @date: 19-4-3 14:44
*/
)
@Data
{
/**
* value: 表頭名稱
* index: 列的號, 0表示第一列
*/
)
;
)
;
)
;
}
2、調用方法 ;
{
ArrayList;
{
TableHeaderExcelProperty tableHeaderExcelProperty ;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
list;
}
Sheet sheet ;
sheet;
ExcelUtil;
multipleSheelPropety;
multipleSheelPropety;
list1;
}
ExcelUtil;
工具類
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
/**
* @description:
* @author: chenmingjian
* @date: 19-3-18 16:16
*/
@Slf4j
{
;
{
initSheet ;
initSheet;
//設置自適應寬度
initSheet;
}
/**
* 讀取少於1000行數據
* @param filePath 文件絕對路徑
* @return
*/
{
;
}
/**
* 讀小於1000行數據, 帶樣式
* filePath 文件絕對路徑
* initSheet :
* sheetNo: sheet頁碼,默認為1
* headLineMun: 從第幾行開始讀取數據,默認為0, 表示從第一行開始讀取
* clazz: 返回數據List<Object> 中Object的類名
*/
{
{
;
}
sheet ;
InputStream fileStream ;
{
fileStream ;
;
{
log;
{
{
{
fileStream;
}
{
log;
}
}
;
}
/**
* 讀大於1000行數據
* @param filePath 文件覺得路徑
* @return
*/
{
;
}
/**
* 讀大於1000行數據, 帶樣式
* @param filePath 文件覺得路徑
* @return
*/
{
{
;
}
sheet ;
InputStream fileStream ;
{
fileStream ;
ExcelListener excelListener ;
EasyExcelFactory;
;
{
log;
{
{
{
fileStream;
}
{
log;
}
}
;
}
/**
* 生成excle
* @param filePath 絕對路徑, 如:/home/chenmingjian/Downloads/aaa.xlsx
* @param data 數據源
* @param head 表頭
*/
{
;
}
/**
* 生成excle
* @param filePath 絕對路徑, 如:/home/chenmingjian/Downloads/aaa.xlsx
* @param data 數據源
* @param sheet excle頁面樣式
* @param head 表頭
*/
{
sheet ;
{
List;
head;
sheet;
}
OutputStream outputStream ;
ExcelWriter writer ;
{
outputStream ;
writer ;
writer;
{
log;
{
{
{
writer;
}
{
outputStream;
}
{
log;
}
}
}
/**
* 生成excle
* @param filePath 絕對路徑, 如:/home/chenmingjian/Downloads/aaa.xlsx
* @param data 數據源
*/
{
;
}
/**
* 生成excle
* @param filePath 絕對路徑, 如:/home/chenmingjian/Downloads/aaa.xlsx
* @param data 數據源
* @param sheet excle頁面樣式
*/
{
{
;
}
sheet ;
sheet;
OutputStream outputStream ;
ExcelWriter writer ;
{
outputStream ;
writer ;
writer;
{
log;
{
{
{
writer;
}
{
outputStream;
}
{
log;
}
}
}
/**
* 生成多Sheet的excle
* @param filePath 絕對路徑, 如:/home/chenmingjian/Downloads/aaa.xlsx
* @param multipleSheelPropetys
*/
{
{
;
}
OutputStream outputStream ;
ExcelWriter writer ;
{
outputStream ;
writer ;
{
Sheet sheet ;
{
sheet;
}
writer;
}
{
log;
{
{
{
writer;
}
{
outputStream;
}
{
log;
}
}
}
/*********************匿名內部類開始,可以提取出去******************************/
@Data
{
;
;
}
/**
* 解析監聽器,
* 每解析一行會回調invoke()方法。
* 整個excel解析結束會執行doAfterAllAnalysed()方法
*
* @author: chenmingjian
* @date: 19-4-3 14:11
*/
@Getter
@Setter
{
;
/**
* 逐行解析
* object : 當前行的數據
*/
@Override
{
//當前行
// context.getCurrentRowNum()
{
datas;
}
}
/**
* 解析完所有數據後會調用該方法
*/
@Override
{
//解析結束銷毀不用的資源
}
}
/************************匿名內部類結束,可以提取出去***************************/
}
測試類
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
/**
* @description: 測試類
* @author: chenmingjian
* @date: 19-4-4 15:24
*/
@SpringBootTest
)
{
/**
* 讀取少於1000行的excle
*/
.Test
{
String filePath ;
List;
objects;
}
/**
* 讀取少於1000行的excle,可以指定sheet和從幾行讀起
*/
.Test
{
String filePath ;
Sheet sheet ;
List;
objects;
}
/**
* 讀取大於1000行的excle
* 帶sheet參數的方法可參照測試方法readLessThan1000RowBySheet()
*/
.Test
{
String filePath ;
List;
objects;
}
/**
* 生成excle
* 帶sheet參數的方法可參照測試方法readLessThan1000RowBySheet()
*/
.Test
{
String filePath ;
List;
data;
data;
data;
List;
ExcelUtil;
}
/**
* 生成excle, 帶用模型
* 帶sheet參數的方法可參照測試方法readLessThan1000RowBySheet()
*/
.Test
{
String filePath ;
ArrayList;
{
TableHeaderExcelProperty tableHeaderExcelProperty ;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
data;
}
ExcelUtil;
}
/**
* 生成excle, 帶用模型,帶多個sheet
*/
.Test
{
ArrayList;
{
ArrayList;
{
TableHeaderExcelProperty tableHeaderExcelProperty ;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
tableHeaderExcelProperty;
list;
}
Sheet sheet ;
sheet;
ExcelUtil;
multipleSheelPropety;
multipleSheelPropety;
list1;
}
ExcelUtil;
}
/*******************匿名內部類,實際開發中該對像要提取出去**********************/
/**
* @description:
* @author: chenmingjian
* @date: 19-4-3 14:44
*/
)
@Data
{
/**
* value: 表頭名稱
* index: 列的號, 0表示第一列
*/
)
;
)
;
)
;
}
/*******************匿名內部類,實際開發中該對像要提取出去**********************/
}
原文出處: 史上最全的Excel导入导出之easyexcel - 点缀星空 - CSDN博客
|
|
|
冷日
(冷日) |
發表時間:2019/7/24 14:29 |
- Webmaster


- 註冊日: 2008/2/19
- 來自:
- 發表數: 15773
|
- [轉貼]JAVA 解析 Excel 工具
Java解析、生成Excel比較有名的框架有Apache poi、jxl。但他們都存在一個嚴重的問題就是非常的耗內存,poi有一套SAX模式的API可以一定程度的解決一些內存溢出的問題,但POI還是有一些缺陷,比如07版Excel解壓縮以及解壓後存儲都是在內存中完成的,內存消耗依然很大。
easyexcel重寫了poi對07版Excel的解析,能夠原本一個3M的excel用POI sax依然需要100M左右內存降低到KB級別,並且再大的excel不會出現內存溢出,03版依賴POI的sax模式。在上層做了模型轉換的封裝,讓使用者更加簡單方便 環境 Java 1.7 +maven 3.0.5 +1. 準備pom.xml
com.alibaba
easyexcel
{latestVersion}
目前最新版本是1.1.1(2018-11-5)
注意: 該版本下使用的POI版本為3.17,所以當項目中的POI版本不為3.17時(有可能項目之前已經引入POI,easyexcel默認自帶版本為3.17),可以考慮升級或者參考文末方法 2. 創建實體假設Excel中列表為
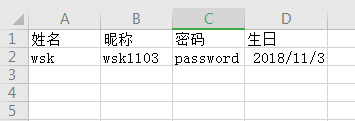 先創建相應的實體User.java @Data
public class User extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名", index = 0)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(value = "暱稱", index = 1)
private String nickName;
@ExcelProperty(value = "密碼", index = 2)
private String password;
@ExcelProperty(value = "生日", index = 3, format = "yyyy/MM/dd")
private Date birthday;
}
注意,該實體必須繼承 BaseRowModel 3. 編寫監聽類,該類用於返回讀取到的對象/**
* @author WuShukai
* @version V1.0
* @description 處理Excel,將讀取到數據保存為對象並輸出
* @date 2018/11/6 16:44
*/
public class ExcelListener extends AnalysisEventListener {
/**
* 自定義用於暫時存儲data。
* 可以通過實例獲取該值
*/
private final List data = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void invoke(T object, AnalysisContext context) {
//數據存儲
data.add(object);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
}
public List getData() {
return data;
}
}
4. 編寫工具類 /**
* 從Excel中讀取文件,讀取的文件是一個DTO類,該類必須繼承BaseRowModel
* 具體實例參考 : MemberMarketDto.java
* 參考:https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel
* 字符流必須支持標記,FileInputStream 不支持標記,可以使用BufferedInputStream 代替
* BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(...));
*
* @param inputStream 文件輸入流
* @param clazz 繼承該類必須繼承BaseRowModel的類
* @return 讀取完成的list
*/
public static List readExcel(final InputStream inputStream, final Class clazz) {
if (null == inputStream) {
throw new NullPointerException("the inputStream is null!");
}
AnalysisEventListener listener = new ExcelListener();
//讀取xls 和 xlxs格式
//如果POI版本為3.17,可以如下聲明
ExcelReader reader = new ExcelReader(inputStream, null, listener);
//判斷格式,針對POI版本低於3.17
//ExcelTypeEnum excelTypeEnum = valueOf(inputStream);
//ExcelReader reader = new ExcelReader(inputStream, excelTypeEnum, null, listener);
reader.read(new com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet(1, 1, clazz));
return ((ExcelListener) listener).getData();
}
/**
* 需要寫入的Excel,有模型映射關係
*
* @param file 需要寫入的Excel,格式為xlsx
* @param list 寫入Excel中的所有數據,繼承於BaseRowModel
*/
public static void writeExcel(final File file, List list) {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
try {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
//寫第一個sheet, 有模型映射關係
Class t = list.get(0).getClass();
com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet sheet = new com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet(1, 0, t);
writer.write(list, sheet);
writer.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 根據輸入流,判斷為xls還是xlsx,該方法原本存在於easyexcel 1.1.0 的ExcelTypeEnum中。
* 如果POI版本為3.17以下,則FileMagic會報錯,找不到該類,此時去到POI 3.17中將FileMagic抽取出來
*/
public static ExcelTypeEnum valueOf(InputStream inputStream) {
try {
FileMagic fileMagic = FileMagic.valueOf(inputStream);
if (FileMagic.OLE2.equals(fileMagic)) {
return ExcelTypeEnum.XLS;
}
if (FileMagic.OOXML.equals(fileMagic)) {
return ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("excelTypeEnum can not null");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
5. POI版本過低處理注意:當POI版本低於easyexcel中內置的POI版本不一致的時候,只能使用被聲明為過期的方法 ExcelReader reader = new ExcelReader(inputStream, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX, null, new AnalysisEventListener>() {...});
無法自動判斷Excel為03還是07版本,此時可以將缺少POI 3.17 中的方法拷貝出來使用。
/**
* @author WuShukai
* @version V1.0
* @description 判斷格式,這個枚舉存在於poi 3.17,但是目前版本是3.15,所以從3.17抽出來使用
* @date 2018/11/6 16:46
*/
public enum FileMagic {
/**
* OLE2 / BIFF8+ stream used for Office 97 and higher documents
*/
OLE2(HeaderBlockConstants._signature),
/**
* OOXML / ZIP stream
*/
OOXML(org.apache.poi.poifs.common.POIFSConstants.OOXML_FILE_HEADER),
/**
* UNKNOWN magic
*/
UNKNOWN(new byte[0]);
final byte[][] magic;
FileMagic(long magic) {
this.magic = new byte[1][8];
LittleEndian.putLong(this.magic[0], 0, magic);
}
FileMagic(byte[]... magic) {
this.magic = magic;
}
public static FileMagic valueOf(byte[] magic) {
for (FileMagic fm : values()) {
int i = 0;
boolean found = true;
for (byte[] ma : fm.magic) {
for (byte m : ma) {
byte d = magic[i++];
if (!(d == m || (m == 0x70 && (d == 0x10 || d == 0x20 || d == 0x40)))) {
found = false;
break;
}
}
if (found) {
return fm;
}
}
}
return UNKNOWN;
}
/**
* @param inp An InputStream which supports either mark/reset
*/
public static FileMagic valueOf(InputStream inp) throws IOException {
if (!inp.markSupported()) {
throw new IOException("getFileMagic() only operates on streams which support mark(int)");
}
// Grab the first 8 bytes
byte[] data = IOUtils.peekFirst8Bytes(inp);
return FileMagic.valueOf(data);
}
}
6. InputStream無法標記錯誤,error for mark(in);因為FileInputStream是無法被標記的,可以將FileInputStream替換成BufferedInputStream。 try(BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) {
do something...
}
原文出處: 使用easyexcel读写Excel - Sky`s Blog
|
|
|
|
|
冷日
(冷日) |
發表時間:2019/7/24 14:38 |
- Webmaster


- 註冊日: 2008/2/19
- 來自:
- 發表數: 15773
|
- [轉貼]Java解析excel工具easyexcel 助你快速簡單避免OOM
Java解析excel工具easyexcel 助你快速簡單避免OOMJava解析、生成Excel比較有名的框架有Apache poi、jxl。但他們都存在一個嚴重的問題就是非常的耗內存,poi有一套SAX模式的API可以一定程度的解決一些內存溢出的問題,但POI還是有一些缺陷,比如07版Excel解壓縮以及解壓後存儲都是在內存中完成的,內存消耗依然很大。easyexcel重寫了poi對07版Excel的解析,能夠原本一個3M的excel用POI sax依然需要100M左右內存降低到KB級別,並且再大的excel不會出現內存溢出,03版依賴POI的sax模式。在上層做了模型轉換的封裝,讓使用者更加簡單方便 easyexcel核心功能 - 讀任意大小的03、07版Excel不會OOM
- 讀Excel自動通過註解,把結果映射為java模型
- 讀Excel支持多sheet
- 讀Excel時候是否對Excel內容做trim()增加容錯
- 寫小量數據的03版Excel(不要超過2000行)
- 寫任意大07版Excel不會OOM
- 寫Excel通過註解將表頭自動寫入Excel
- 寫Excel可以自定義Excel樣式 如:字體,加粗,表頭顏色,數據內容顏色
- 寫Excel到多個不同sheet
- 寫Excel時一個sheet可以寫多個Table
- 寫Excel時候自定義是否需要寫表頭
快速使用1. JAR包依賴 使用前最好咨詢下最新版,或者到mvn倉庫搜索一下easyexcel的最新版
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>{latestVersion}</version>
</dependency>
2. 讀取Excel 使用easyexcel解析03、07版本的Excel只是ExcelTypeEnum不同,其他使用完全相同,使用者無需知道底層解析的差異。 無java模型直接把excel解析的每行結果以List返回 在ExcelListener獲取解析結果
讀excel代碼示例如下:
@Test
public void testExcel2003NoModel() {
InputStream inputStream = getInputStream("loan1.xls");
try {
// 解析每行結果在listener中處理
ExcelListener listener = new ExcelListener();
ExcelReader excelReader = new ExcelReader(inputStream, ExcelTypeEnum.XLS, null, listener);
excelReader.read();
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ExcelListener示例代碼如下:
/* 解析監聽器,
* 每解析一行會回調invoke()方法。
* 整個excel解析結束會執行doAfterAllAnalysed()方法
*
* 下面只是我寫的一個樣例而已,可以根據自己的邏輯修改該類。
* @author jipengfei
* @date 2017/03/14
*/
public class ExcelListener extends AnalysisEventListener {
//自定義用於暫時存儲data。
//可以通過實例獲取該值
private List<Object> datas = new ArrayList<Object>();
public void invoke(Object object, AnalysisContext context) {
System.out.println("當前行:"+context.getCurrentRowNum());
System.out.println(object);
datas.add(object);//數據存儲到list,供批量處理,或後續自己業務邏輯處理。
doSomething(object);//根據自己業務做處理
}
private void doSomething(Object object) {
//1、入庫調用接口
}
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
// datas.clear();//解析結束銷毀不用的資源
}
public List<Object> getDatas() {
return datas;
}
public void setDatas(List<Object> datas) {
this.datas = datas;
}
}
有java模型映射
java模型寫法如下:
public class LoanInfo extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(index = 0)
private String bankLoanId;
@ExcelProperty(index = 1)
private Long customerId;
@ExcelProperty(index = 2,format = "yyyy/MM/dd")
private Date loanDate;
@ExcelProperty(index = 3)
private BigDecimal quota;
@ExcelProperty(index = 4)
private String bankInterestRate;
@ExcelProperty(index = 5)
private Integer loanTerm;
@ExcelProperty(index = 6,format = "yyyy/MM/dd")
private Date loanEndDate;
@ExcelProperty(index = 7)
private BigDecimal interestPerMonth;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"一級表頭","二級表頭"})
private BigDecimal sax;
}
@ExcelProperty(index = 3)數字代表該字段與excel對應列號做映射,也可以採用 @ExcelProperty(value = {「一級表頭」,」二級表頭」})用於解決不確切知道excel第幾列和該字段映射,位置不固定,但表頭的內容知道的情況。
@Test
public void testExcel2003WithReflectModel() {
InputStream inputStream = getInputStream("loan1.xls");
try {
// 解析每行結果在listener中處理
AnalysisEventListener listener = new ExcelListener();
ExcelReader excelReader = new ExcelReader(inputStream, ExcelTypeEnum.XLS, null, listener);
excelReader.read(new Sheet(1, 2, LoanInfo.class));
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
帶模型解析與不帶模型解析主要在構造new Sheet(1, 2, LoanInfo.class)時候包含class。Class需要繼承BaseRowModel暫時BaseRowModel沒有任何內容,後面升級可能會增加一些默認的數據。 3. 生成Excel 每行數據是List無表頭
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("/Users/jipengfei/77.xlsx");
try {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX,false);
//寫第一個sheet, sheet1 數據全是List<String> 無模型映射關係
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0);
sheet1.setSheetName("第一個sheet");
writer.write(getListString(), sheet1);
writer.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
每行數據是一個java模型有表頭—-表頭層級為一 生成Excel格式如下圖:
 模型寫法如下:
public class ExcelPropertyIndexModel extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名" ,index = 0)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(value = "年齡",index = 1)
private String age;
@ExcelProperty(value = "郵箱",index = 2)
private String email;
@ExcelProperty(value = "地址",index = 3)
private String address;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性別",index = 4)
private String sax;
@ExcelProperty(value = "高度",index = 5)
private String heigh;
@ExcelProperty(value = "備註",index = 6)
private String last;
}
@ExcelProperty(value = 「姓名」,index = 0) value是表頭數據,默認會寫在excel的表頭位置,index代表第幾列。
@Test
public void test1() throws FileNotFoundException {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("/Users/jipengfei/78.xlsx");
try {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
//寫第一個sheet, sheet1 數據全是List<String> 無模型映射關係
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0,ExcelPropertyIndexModel.class);
writer.write(getData(), sheet1);
writer.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
每行數據是一個java模型有表頭—-表頭層級為多層級 生成Excel格式如下圖:  java模型寫法如下:
public class MultiLineHeadExcelModel extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭1","表頭1","表頭31"},index = 0)
private String p1;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭1","表頭1","表頭32"},index = 1)
private String p2;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭3","表頭3","表頭3"},index = 2)
private int p3;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭4","表頭4","表頭4"},index = 3)
private long p4;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭5","表頭51","表頭52"},index = 4)
private String p5;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭6","表頭61","表頭611"},index = 5)
private String p6;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭6","表頭61","表頭612"},index = 6)
private String p7;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭6","表頭62","表頭621"},index = 7)
private String p8;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"表頭6","表頭62","表頭622"},index = 8)
private String p9;
}
寫Excel寫法同上,只需將ExcelPropertyIndexModel.class改為MultiLineHeadExcelModel.class 一個Excel多個sheet寫法
@Test
public void test1() throws FileNotFoundException {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("/Users/jipengfei/77.xlsx");
try {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX,false);
//寫第一個sheet, sheet1 數據全是List<String> 無模型映射關係
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0);
sheet1.setSheetName("第一個sheet");
writer.write(getListString(), sheet1);
//寫第二個sheet sheet2 模型上打有表頭的註解,合併單元格
Sheet sheet2 = new Sheet(2, 3, MultiLineHeadExcelModel.class, "第二個sheet", null);
sheet2.setTableStyle(getTableStyle1());
writer.write(getModeldatas(), sheet2);
//寫sheet3 模型上沒有註解,表頭數據動態傳入
List<List<String>> head = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> headCoulumn1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn2 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn3 = new ArrayList<String>();
headCoulumn1.add("第一列");
headCoulumn2.add("第二列");
headCoulumn3.add("第三列");
head.add(headCoulumn1);
head.add(headCoulumn2);
head.add(headCoulumn3);
Sheet sheet3 = new Sheet(3, 1, NoAnnModel.class, "第三個sheet", head);
writer.write(getNoAnnModels(), sheet3);
writer.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
一個sheet中有多個表格
@Test
public void test2() throws FileNotFoundException {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("/Users/jipengfei/77.xlsx");
try {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX,false);
//寫sheet1 數據全是List<String> 無模型映射關係
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0);
sheet1.setSheetName("第一個sheet");
Table table1 = new Table(1);
writer.write(getListString(), sheet1, table1);
writer.write(getListString(), sheet1, table1);
//寫sheet2 模型上打有表頭的註解
Table table2 = new Table(2);
table2.setTableStyle(getTableStyle1());
table2.setClazz(MultiLineHeadExcelModel.class);
writer.write(getModeldatas(), sheet1, table2);
//寫sheet3 模型上沒有註解,表頭數據動態傳入,此情況下模型field順序與excel現實順序一致
List<List<String>> head = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> headCoulumn1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn2 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn3 = new ArrayList<String>();
headCoulumn1.add("第一列");
headCoulumn2.add("第二列");
headCoulumn3.add("第三列");
head.add(headCoulumn1);
head.add(headCoulumn2);
head.add(headCoulumn3);
Table table3 = new Table(3);
table3.setHead(head);
table3.setClazz(NoAnnModel.class);
table3.setTableStyle(getTableStyle2());
writer.write(getNoAnnModels(), sheet1, table3);
writer.write(getNoAnnModels(), sheet1, table3);
writer.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4. 測試數據分析   

從上面的性能測試可以看出easyexcel在解析耗時上比poiuserModel模式弱了一些。主要原因是我內部採用了反射做模型字段映射,中間我也加了cache,但感覺這點差距可以接受的。但在內存消耗上差別就比較明顯了,easyexcel在後面文件再增大,內存消耗幾乎不會增加了。但poi userModel就不一樣了,簡直就要爆掉了。想想一個excel解析200M,同時有20個人再用估計一台機器就掛了。 5. 百萬數據解析對比 easyexcel解析百萬數據內存圖如下:
 poi解析百萬數據內存圖如下:
 從上面兩圖可以看出,easyexcel解析時內存消耗很少,最多消耗不到50M;POI解析過程中直接飄升到1.5G左右,系統內存耗盡,程序掛掉。 GitHub地址: https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel
原文出處: Java解析excel工具easyexcel 助你快速简单避免OOM - 红豆和绿豆的博客 - CSDN博客
|
|
|
|
















